
AVAILABLE PRESSFIT PINS
0.50x0.40 mmFin 74-91 NFout 54-73 NPCB hole ∅0.60
0.64x0.64 mmFin <100 NFout >20 NPCB hole ∅1
0.6x1.0 mmFin 66–135 NFout 145–235 NPCB hole ∅1.25
0.6x1.5 mm
0.8x1.5 mm
VORTEILE VON PRESSFIT-STIFTEN
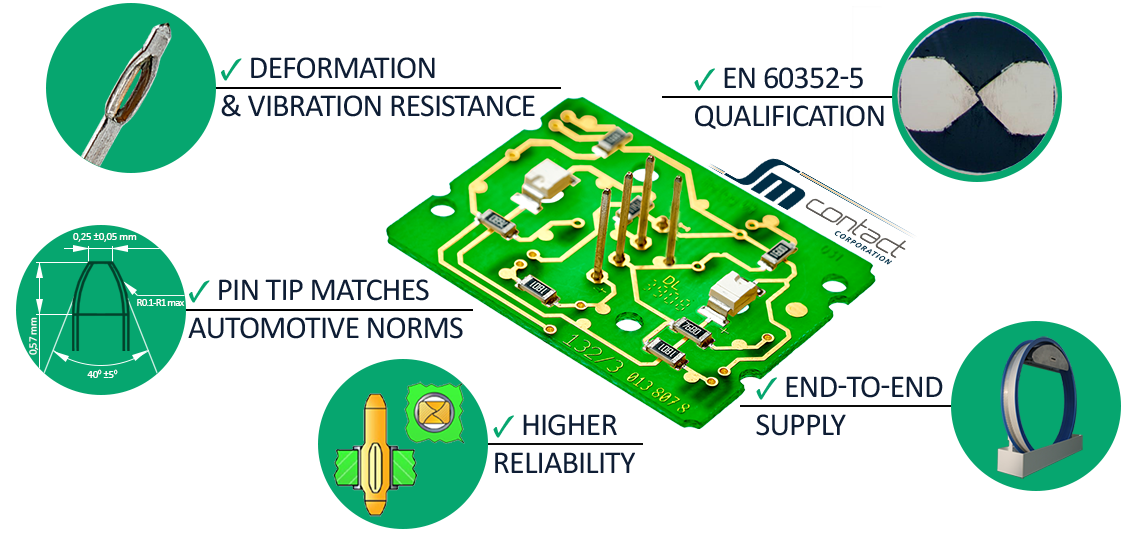
Higher reliability
Size difference between PCB hole and Pressfit zone leads to Pressfit deformation during insertion. Compression of a pin guarantees reliable connection.

Qualification
Pressfit pins 0.50×0.40 mm, 0.60×1.00 mm, 0.60×0.60 mm, 1.2×0.6 mm are qualified in accordance to EN 60352-5. It proved to have required contact resistance (< 0.5 mΩ), acceptable deformations and resistance to rapid temperature changes and climate sequences.
Deformation and vibrations resistance
Pin insertion doesn’t require additional soldering which means no thermal stress and no damage for components. As a result connection stays reliable under vibrations.


End-to-end supply
Reel is compact and easy to change. It fits all pin types and sizes. Compared to the bandolier pins, there is no excess material left from the end-to-end pins. No need to buy a new reel every time the pins run out: the reel is rechargeable. Only SM Contact supplies 0.4*0.5 Pressfit pins as end-to-end.
PRESSFIT EN 60352-5 QUALIFICATION
✓ ΔRc < 0.5 mΩ
*Technical reports could be presented on your request
✓ No cracks
✓ amax < 70 µm (drilled hole contour deformation)
✓ bmin > 8 µm (remaining thickness of the plating)
✓ cmax < 50 µm (outer layer deformation)
*Technical reports could be presented on your request
✓ 10 cycles
✓ −40 °C/+85 °C
✓ t1 = 30 min
*Technical reports could be presented on your request
✓ +85 °C, 16 h
✓ +25 °C/+55 °C, 90% RH/95% RH
✓ −40 °C, 2 h
*Technical reports could be presented on your request

Press-in force measurement
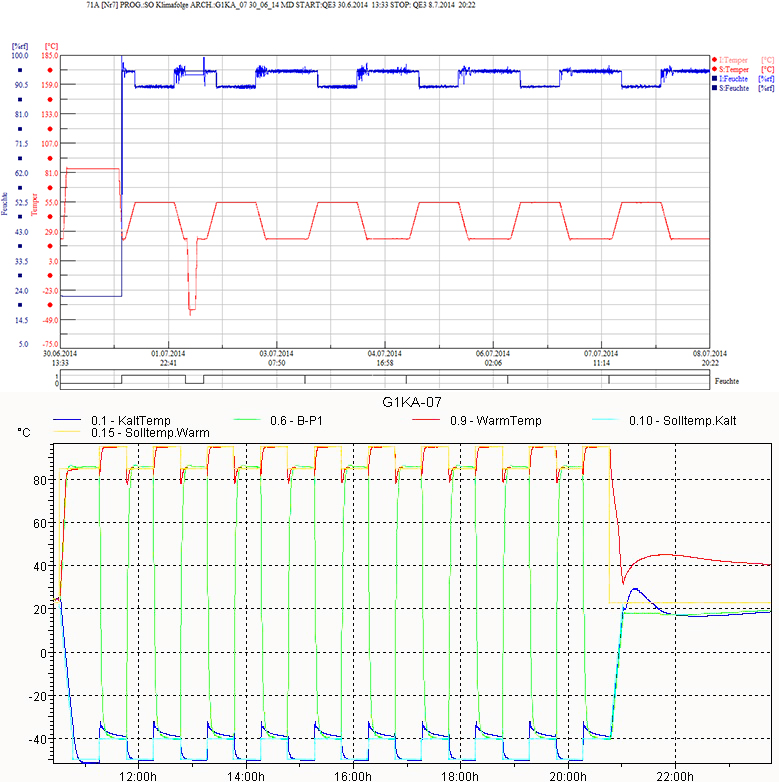
Temperature and humidity recording
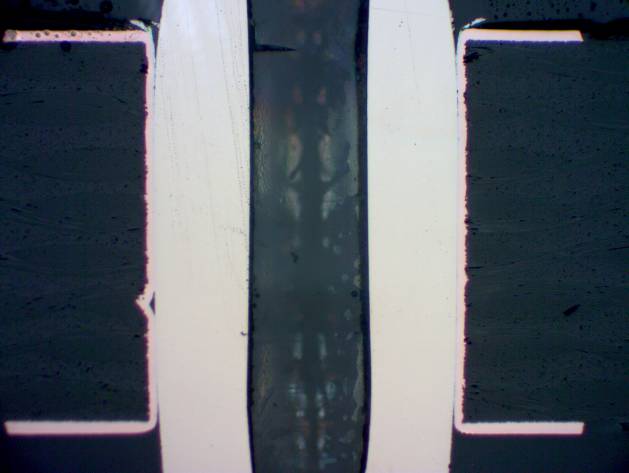

Longitudinal sectioning

Transverse sectioning